Table des matières
PART 03 : Lines and circles
Greetings! This is the third part of the VGA Trainer series! Sorry it took so long to get out, but I had a running battle with the traffic department for three days to get my car registered, and then the MailBox went down. Ahh, well, life stinks. Anyway, today will do some things vital to most programs : Lines and circles.
Watch out for next week's part : Virtual screens. The easy way to eliminate flicker, “doubled sprites”, and subjecting the user to watch you building your screen. Almost every ASPHYXIA demo has used a virtual screen (with the exception of the SilkyDemo), so this is one to watch out for. I will also show you how to put all of these loose procedures into units.
If you would like to contact me, or the team, there are many ways you can do it :
- Write a message to Grant Smith in private mail here on the Mailbox BBS.
- Write a message here in the Programming conference here on the Mailbox (Preferred if you have a general programming query or problem others would benefit from)
- Write to ASPHYXIA on the ASPHYXIA BBS.
- Write to Denthor, Eze or Livewire on Connectix.
- Write to :
Grant Smith P.O.Box 270 Kloof 3640
- Call me (Grant Smith) at 73 2129 (leave a message if you call during varsity)
NB : If you are a representative of a company or BBS, and want ASPHYXIA to do you a demo, leave mail to me; we can discuss it. NNB : If you have done/attempted a demo, SEND IT TO ME! We are feeling quite lonely and want to meet/help out/exchange code with other demo groups. What do you have to lose? Leave a message here and we can work out how to transfer it. We really want to hear from you!
Circle Algorithim
You all know what a circle looks like. But how do you draw one on the computer?
You probably know circles drawn with the degrees at these points :
0
▄█|█▄
███|███
270 ----+---- 90
███|███
▀█|█▀
180
Sorry about my ASCI 
270
▄█|█▄
███|███
180 ----+---- 0
███|███
▀█|█▀
90
Even so, we can still use the famous equations to draw our circle … (You derive the following by using the theorem of our good friend Pythagoras)
Sin (deg) = Y/R
Cos (deg) = X/R
(This is standard 8(?) maths … if you haven't reached that level yet, take this to your dad, or if you get stuck leave me a message and I'll do a bit of basic Trig with you. I aim to please 
Where Y = your Y-coord
X = your X-coord
R = your radius (the size of your circle)
deg = the degree
To simplify matters, we rewrite the equation to get our X and Y values :
Y = R*Sin(deg)
X = R*Cos(deg)
This obviousy is perfect for us, because it gives us our X and Y co-ords to put into our putpixel routine (see Part 1). Because the Sin and Cos functions return a Real value, we use a round function to transform it into an Integer.
Procedure Circle (oX,oY,rad:integer;Col:Byte); VAR deg:real; X,Y:integer; BEGIN deg:=0; repeat X:=round(rad*COS (deg)); Y:=round(rad*sin (deg)); putpixel (x+ox,y+oy,Col); deg:=deg+0.005; until (deg>6.4); END;
In the above example, the smaller the amount that deg is increased by, the closer the pixels in the circle will be, but the slower the procedure.
0.005 seem to be best for the 320×200 screen.
ASPHYXIA does not use this particular circle algorithm, ours is in assembly language, but this one should be fast enough for most. If it isn't, give us the stuff you are using it for and we'll give you ours.
Line algorithms
There are many ways to draw a line on the computer. I will describe one and give you two. (The second one you can figure out for yourselves; it is based on the first one but is faster)
The first thing you need to do is pass what you want the line to look like to your line procedure. What I have done is said that x1,y1 is the first point on the screen, and x2,y2 is the second point. We also pass the color to the procedure. (Remember the screens top left hand corner is (0,0); see Part 1)
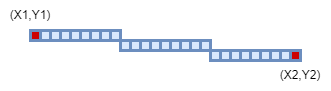
Again, sorry about my drawings 
To find the length of the line, we say the following :
XLength = ABS (x1-x2)
YLength = ABS (y1-y2)
The ABS function means that whatever the result, it will give you an absolute, or posotive, answer. At this stage I set a variable stating wheter the difference between the two x's are negative, zero or posotive.
(I do the same for the y's) If the difference is zero, I just use a loop keeping the two with the zero difference posotive, then exit.
If neither the x's or y's have a zero difference, I calculate the X and Y slopes, using the following two equations :
Xslope = Xlength / Ylength
Yslope = Ylength / Xlength
As you can see, the slopes are real numbers.
XSlope = 1 / YSlope
Now, there are two ways of drawing the lines :
X = XSlope * Y
Y = YSlope * X
The question is, which one to use? if you use the wrong one, your line will look like this :

Instead of this :

Well, the solution is as follows :
*\``|``/* ***\|/*** ----+---- ***/|\*** */``|``\*
If the slope angle is in the area of the stars (*) then use the first equation, if it is in the other section (`) then use the second one.
What you do is you calculate the variable on the left hand side by putting the variable on the right hand side in a loop and solving. Below is our finished line routine :
function:
Procedure Line (x1,y1,x2,y2:integer;col:byte); VAR x,y,xlength,ylength,dx,dy:integer; xslope,yslope:real; BEGIN xlength:=abs (x1-x2); if (x1-x2)<0 then dx:=-1; if (x1-x2)=0 then dx:=0; if (x1-x2)>0 then dx:=+1; ylength:=abs (y1-y2); if (y1-y2)<0 then dy:=-1; if (y1-y2)=0 then dy:=0; if (y1-y2)>0 then dy:=+1; if (dy=0) then BEGIN if dx<0 then for x:=x1 to x2 do putpixel (x,y1,col); if dx>0 then for x:=x2 to x1 do putpixel (x,y1,col); exit; END; if (dx=0) then BEGIN if dy<0 then for y:=y1 to y2 do putpixel (x1,y,col); if dy>0 then for y:=y2 to y1 do putpixel (x1,y,col); exit; END; xslope:=xlength/ylength; yslope:=ylength/xlength; if (yslope/xslope<1) and (yslope/xslope>-1) then BEGIN if dx<0 then for x:=x1 to x2 do BEGIN y:= round (yslope*x); putpixel (x,y,col); END; if dx>0 then for x:=x2 to x1 do BEGIN y:= round (yslope*x); putpixel (x,y,col); END; END ELSE BEGIN if dy<0 then for y:=y1 to y2 do BEGIN x:= round (xslope*y); putpixel (x,y,col); END; if dy>0 then for y:=y2 to y1 do BEGIN x:= round (xslope*y); putpixel (x,y,col); END; END; END;
Quite big, isn't it? Here is a much shorter way of doing much the same thing :
function sgn(a:real):integer; begin if a>0 then sgn:=+1; if a<0 then sgn:=-1; if a=0 then sgn:=0; end; procedure line(a,b,c,d,col:integer); var u,s,v,d1x,d1y,d2x,d2y,m,n:real; i:integer; begin u:= c - a; v:= d - b; d1x:= SGN(u); d1y:= SGN(v); d2x:= SGN(u); d2y:= 0; m:= ABS(u); n := ABS(v); IF NOT (M>N) then BEGIN d2x := 0 ; d2y := SGN(v); m := ABS(v); n := ABS(u); END; s := INT(m / 2); FOR i := 0 TO round(m) DO BEGIN putpixel(a,b,col); s := s + n; IF not (s<m) THEN BEGIN s := s - m; a:= a +round(d1x); b := b + round(d1y); END ELSE BEGIN a := a + round(d2x); b := b + round(d2y); END; end; END;
This routine is very fast, and should meet almost all of your requirements (ASPHYXIA used it for quite a while before we made our new one.) In the end program, both the new line routine and the circle routine are tested. A few of the procedures of the first parts are also used.
Line and circle routines may seem like fairly trivial things, but they are a vital component of many programs, and you may like to look up other methods of drawing them in books in the library (I know that here at the varsity they have books for doing this kind of stuff all over the place) A good line routine to look out for is the Bressenhams line routine … there is a Bressenhams circle routine too … I have documentaiton for them if anybody is interested, they are by far some of the fastest routines you will use.
In closing
Varsity has started again, so I am (shock) going to bed before three in the morning, so my quote this week wasn't written in the same wasted way my last weeks one was (For last week's one, I had gotten 8 hours sleep in 3 days, and thought up and wrote the quote at 2:23 am before I fell asleep.)
[ "What does it do?" she asks.
"It's a computer," he replies.
"Yes, dear, but what does it do?"
"It ..er.. computes! It's a computer."
"What does it compute?"
"What? Er? Um. Numbers! Yes, numbers!" He smiles worriedly.
"Why?"
"Why? Well ..um.. why?" He starts to sweat.
"I mean, is it just something to dust around, or does it actually do something useful?"
"Um...you can call other computers with it!" Hope lights up his eyes. "So you can get programs from other computers!"
"I see. Tell me, what do these programs do?"
"Do? I don't think I fol..."
"I see. They compute. Numbers. For no particular reason." He withers under her gaze.
"Yes, but..."
She smiles, and he trails off, defeated. She takes another look at the thing. "Although," she says, with a strange look in her eyes. He looks up, an insane look of hope on his face. "Does it come in pink?" she asks.
- Grant Smith
Tue 27 July, 1993
9:35 pm.
Code Source
PASCAL
(*****************************************************************************) (* *) (* TUT3.PAS - VGA Trainer Program 3 (in Pascal) *) (* *) (* "The VGA Trainer Program" is written by Denthor of Asphyxia. However it *) (* was limited to Pascal only in its first run. All I have done is taken *) (* his original release, translated it to C++, and touched up a few things. *) (* I take absolutely no credit for the concepts presented in this code, and *) (* am NOT the person to ask for help if you are having trouble. *) (* *) (* Program Notes : This program presents many new concepts, including: *) (* Cirle and Line algorithms. *) (* *) (* Author : Grant Smith (Denthor) - denthor@beastie.cs.und.ac.za *) (* *) (*****************************************************************************) {$X+} USES crt; CONST VGA = $a000; VAR loop1:integer; Pall : Array [1..199,1..3] of byte; { This is our temporary pallette. We ony use colors 1 to 199, so we only have variables for those ones. } {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure SetMCGA; { This procedure gets you into 320x200x256 mode. } BEGIN asm mov ax,0013h int 10h end; END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure SetText; { This procedure returns you to text mode. } BEGIN asm mov ax,0003h int 10h end; END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure Putpixel (X,Y : Integer; Col : Byte); { This puts a pixel on the screen by writing directly to memory. } BEGIN Mem [VGA:X+(Y*320)]:=Col; END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} procedure WaitRetrace; assembler; label l1, l2; asm mov dx,3DAh l1: in al,dx and al,08h jnz l1 l2: in al,dx and al,08h jz l2 end; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure Pal(ColorNo : Byte; R,G,B : Byte); { This sets the Red, Green and Blue values of a certain color } Begin Port[$3c8] := ColorNo; Port[$3c9] := R; Port[$3c9] := G; Port[$3c9] := B; End; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure Circle (X,Y,rad:integer;Col:Byte); { This draws a circle with centre X,Y, with Rad as it's radius } VAR deg:real; BEGIN deg:=0; repeat X:=round(rad*COS (deg)); Y:=round(rad*sin (deg)); putpixel (x+160,y+100,col); deg:=deg+0.005; until (deg>6.4); END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure Line2 (x1,y1,x2,y2:integer;col:byte); { This draws a line from x1,y1 to x2,y2 using the first method } VAR x,y,xlength,ylength,dx,dy:integer; xslope,yslope:real; BEGIN xlength:=abs (x1-x2); if (x1-x2)<0 then dx:=-1; if (x1-x2)=0 then dx:=0; if (x1-x2)>0 then dx:=+1; ylength:=abs (y1-y2); if (y1-y2)<0 then dy:=-1; if (y1-y2)=0 then dy:=0; if (y1-y2)>0 then dy:=+1; if (dy=0) then BEGIN if dx<0 then for x:=x1 to x2 do putpixel (x,y1,col); if dx>0 then for x:=x2 to x1 do putpixel (x,y1,col); exit; END; if (dx=0) then BEGIN if dy<0 then for y:=y1 to y2 do putpixel (x1,y,col); if dy>0 then for y:=y2 to y1 do putpixel (x1,y,col); exit; END; xslope:=xlength/ylength; yslope:=ylength/xlength; if (yslope/xslope<1) and (yslope/xslope>-1) then BEGIN if dx<0 then for x:=x1 to x2 do BEGIN y:= round (yslope*x); putpixel (x,y,col); END; if dx>0 then for x:=x2 to x1 do BEGIN y:= round (yslope*x); putpixel (x,y,col); END; END ELSE BEGIN if dy<0 then for y:=y1 to y2 do BEGIN x:= round (xslope*y); putpixel (x,y,col); END; if dy>0 then for y:=y2 to y1 do BEGIN x:= round (xslope*y); putpixel (x,y,col); END; END; END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} procedure line(a,b,c,d,col:integer); { This draws a line from x1,y1 to x2,y2 using the first method } function sgn(a:real):integer; begin if a>0 then sgn:=+1; if a<0 then sgn:=-1; if a=0 then sgn:=0; end; var u,s,v,d1x,d1y,d2x,d2y,m,n:real; i:integer; begin u:= c - a; v:= d - b; d1x:= SGN(u); d1y:= SGN(v); d2x:= SGN(u); d2y:= 0; m:= ABS(u); n := ABS(v); IF NOT (M>N) then BEGIN d2x := 0 ; d2y := SGN(v); m := ABS(v); n := ABS(u); END; s := INT(m / 2); FOR i := 0 TO round(m) DO BEGIN putpixel(a,b,col); s := s + n; IF not (s<m) THEN BEGIN s := s - m; a:= a +round(d1x); b := b + round(d1y); END ELSE BEGIN a := a + round(d2x); b := b + round(d2y); END; end; END; {ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ} Procedure PalPlay; { This procedure mucks about with our "virtual pallette", then shoves it to screen. } Var Tmp : Array[1..3] of Byte; { This is used as a "temporary color" in our pallette } loop1 : Integer; BEGIN Move(Pall[199],Tmp,3); { This copies color 199 from our virtual pallette to the Tmp variable } Move(Pall[1],Pall[2],198*3); { This moves the entire virtual pallette up one color } Move(Tmp,Pall[1],3); { This copies the Tmp variable to the bottom of the virtual pallette } WaitRetrace; For loop1:=1 to 199 do pal (loop1,pall[loop1,1],pall[loop1,2],pall[loop1,3]); END; BEGIN ClrScr; Writeln ('This sample program will test out our line and circle algorithms.'); Writeln ('In the first part, many circles will be draw creating (hopefully)'); Writeln ('a "tunnel" effect. I will the rotate the pallete to make it look'); Writeln ('nice. I will then draw some lines and rotate the pallette on them'); Writeln ('too. Note : I am using the slower (first) line algorithm (in'); Writeln ('procedure line2). Change it to Procedure Line and it will be using'); Writeln ('the second line routine. NB : For descriptions on how pallette works'); Writeln ('have a look at part two of this series; I won''t re-explain it here.'); Writeln; Writeln ('Remember to send me any work you have done, I am most eager to help.'); Writeln; Writeln; Writeln ('Hit any key to continue ...'); Readkey; setmcga; For Loop1 := 1 to 199 do BEGIN Pall[Loop1,1] := Loop1 mod 30+33; Pall[Loop1,2] := 0; Pall[Loop1,3] := 0; END; { This sets colors 1 to 199 to values between 33 to 63. The MOD function gives you the remainder of a division, ie. 105 mod 10 = 5 } WaitRetrace; For loop1:=1 to 199 do pal (loop1,pall[loop1,1],pall[loop1,2],pall[loop1,3]); { This sets the true pallette to variable Pall } for loop1:=1 to 90 do circle (160,100,loop1,loop1); { This draws 90 circles all with centres at 160,100; with increasing radii and colors. } Repeat PalPlay; Until keypressed; Readkey; for loop1:=1 to 199 do line2 (0,1,319,loop1,loop1); { *** Replace Line2 with Line to use the second line algorithm *** } { This draws 199 lines, all starting at 0,1 } Repeat PalPlay; Until keypressed; readkey; SetText; Writeln ('All done. Okay, so maybe it wasn''t a tunnel effect, but you get the'); Writeln ('general idea ;-) This concludes the third sample program in the ASPHYXIA'); Writeln ('Training series. You may reach DENTHOR under the name of GRANT SMITH'); Writeln ('on the MailBox BBS, or leave a message to ASPHYXIA on the ASPHYXIA BBS.'); Writeln ('Get the numbers from Roblist, or write to :'); Writeln (' Grant Smith'); Writeln (' P.O. Box 270'); Writeln (' Kloof'); Writeln (' 3640'); Writeln ('I hope to hear from you soon!'); Writeln; Writeln; Write ('Hit any key to exit ...'); Readkey; END.
C
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // TUTPROG3.CPP - VGA Trainer Program 3 (in Turbo C++ 3.0) // // // // "The VGA Trainer Program" is written by Denthor of Asphyxia. However it // // was limited to Pascal only in its first run. All I have done is taken // // his original release, translated it to C++ and touched up a few things. // // I take absolutely no credit for the concepts presented in this code and // // am NOT the person to ask for help if you are having trouble. // // // // Program Notes : This program presents many new concepts, including: // // Cirle and Line algorithms. // // // // If you are compiling this code command line, be sure to // // use the "-ml" parameter (large memory model). // // Otherwise, the program will compile and link, but will // // lock up your system. // // // // Author : Grant Smith (Denthor) - denthor@beastie.cs.und.ac.za // // Translator : Christopher G. Mann - r3cgm@dax.cc.uakron.edu // // // // Last Modified : December 7, 1994 // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // INCLUDE FILES // // // #include <conio.h> // getch(), clrscr(), kbhit() #include <dos.h> // MK_FP, Geninterrupt() #include <math.h> // floor(), ceil(), abs(), sin(), cos() #include <iostream.h> // cout, endl, memset(), _fmemset() // // // FUNCTION PROTOTYPES // // // // MODE SETTING FUNCTIONS void SetMCGA(); void SetText(); // PALLETTE FUNCTIONS void Pal (unsigned char ColorNo, unsigned char R, unsigned char G, unsigned char B); void PalPlay(); // SMALL UTILITY FUNCTIONS int sgn (long a); int round (long a); // DRAWING FUNCTIONS void Putpixel (int x, int y, unsigned char Col); void Line (int a, int b, int c, int d, int col); void Line2 (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int col); void Circle (int X, int Y, int rad, int col); void WaitRetrace(); // // // GLOBAL VARIABLE DECLARATIONS // // // // declare a pointer to the offset of VGA memory unsigned char *vga = (unsigned char *) MK_FP(0xA000, 0); // This declares the PALL variable. 0 to 255 signifies the colors of the // pallette, 1 to 3 signifies the Red, Green and Blue values. I am // going to use this as a sort of "virtual pallette", and alter it // as much as I want, then suddenly bang it to screen. Pall2 is used // to "remember" the origional pallette so that we can restore it at // the end of the program. */ unsigned char Pall[256][3], Pall2[256][3]; /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // MAIN FUNCTION // // // /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void main() { clrscr(); cout << "This sample program will test out our line and circle algorithms.\n" << "In the first part, many circles will be draw creating (hopefully)\n" << "a ""tunnel"" effect. I will the rotate the pallete to make it look\n" << "nice. I will then draw some lines and rotate the pallette on them\n" << "too. Note : I am using the slower (first) line algorithm (in\n" << "procedure line2). Change it to Procedure Line and it will be using\n" << "the second line routine. NB : For descriptions on how pallette works\n" << "have a look at part two of this series; I won''t re-explain it here." << endl << endl; cout << "Remember to send me any work you have done, I am most eager to help." << endl << endl; cout << "Hit any key to continue ..."; getch(); SetMCGA(); // This sets colors 1 to 199 to values between 33 to 63. The MOD // function gives you the remainder of a division, ie. 105 mod 10 = 5 } for (int loop1=1; loop1<200; loop1++) { Pall[loop1][0] = (loop1 % 30) + 33; Pall[loop1][1] = 0; Pall[loop1][2] = 0; } WaitRetrace(); // This sets the true pallette to variable Pall for (loop1=1; loop1<200; loop1++) Pal(loop1, Pall[loop1][0], Pall[loop1][1], Pall[loop1][2]); // This draws 90 circles all with centers at 160,100 with increasing // radii and colors. for (loop1=1; loop1<91; loop1++) Circle(160, 100, loop1, loop1); // wait until a key is pressed while (!kbhit()) PalPlay(); // make sure to clear the keyboard buffer getch(); // This draws 199 lines, all starting at 0,1 for (loop1=1; loop1<200; loop1++) Line2 (0,1,319,loop1,loop1); // *** Replace Line2 with Line to use the // second line algorithm *** while (!kbhit()) PalPlay(); getch(); getch(); SetText(); cout << "All done. Okay, so maybe it wasn''t a tunnel effect, but you get the\n" << "general idea ;-) This concludes the third sample program in the ASPHYXIA\n" << "Training series. You may reach DENTHOR under the name of GRANT SMITH\n" << "on the MailBox BBS, or leave a message to ASPHYXIA on the ASPHYXIA BBS\n" << "Get the numbers from Roblist, or write to :\n" << " Grant Smith\n" << " P.O. Box 270\n" << " Kloof\n" << " 3640\n" << endl; cout << "I hope to hear from you soon!" << endl << endl; cout << "Hit any key to exit ..."; getch(); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // SetMCGA() - This function gets you into 320x200x256 mode. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void SetMCGA() { _AX = 0x0013; geninterrupt (0x10); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // SetText() - This function gets you into text mode. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void SetText() { _AX = 0x0003; geninterrupt (0x10); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // Pal() - This sets the Red, Green, and Blue values of a certain color. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Pal(unsigned char ColorNo, unsigned char R, unsigned char G, unsigned char B) { outp (0x03C8,ColorNo); // here is the pallette color I want to set outp (0x03C9,R); outp (0x03C9,G); outp (0x03C9,B); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // PalPlay() - This function mucks about with our "virtual pallette", then // // shoves it to the screen. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void PalPlay() { unsigned char Tmp[3]; // This copies color 199 from our virtual pallette to the Tmp variable. _fmemmove(Tmp,Pall[199],3); // This moves the entire virtual pallette up one color. _fmemmove(Pall[2],Pall[1],199*3); // This copies the Tmp variable to the bottom of the virtual pallette. // Don't change 0: leave this always black to not change overscan color. _fmemmove(Pall[1],Tmp,3); WaitRetrace(); for (int loop1=0;loop1<256;loop1++) Pal(loop1,Pall[loop1][0], Pall[loop1][1], Pall[loop1][2]); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // sgn() - This function is used by Line() to determine the sign of a long // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// int sgn (long a) { if (a > 0) return +1; else if (a < 0) return -1; else return 0; } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // round() - This function is used by Line() to round a long to the // // nearest integer. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// int round (long a) { if ( (a - (int)a) < 0.5) return floor(a); else return ceil(a); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // Putpixel() - This puts a pixel on the screen by writing directly to // // memory. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Putpixel (int x, int y, unsigned char Col) { memset(vga+(x+(y*320)),Col,1); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // Line() - This draws a line from a,b to c,d of color col. // // This function will be explained in more detail in tut3new.zip // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Line(int a, int b, int c, int d, int col) { long u,s,v,d1x,d1y,d2x,d2y,m,n; int i; u = c-a; // x2-x1 v = d-b; // y2-y1 d1x = sgn(u); // d1x is the sign of u (x2-x1) (VALUE -1,0,1) d1y = sgn(v); // d1y is the sign of v (y2-y1) (VALUE -1,0,1) d2x = sgn(u); // d2x is the sign of u (x2-x1) (VALUE -1,0,1) d2y = 0; m = abs(u); // m is the distance between x1 and x2 n = abs(v); // n is the distance between y1 and y2 if (m<=n) { // if the x distance is greater than the y distance d2x = 0; d2y = sgn(v); // d2y is the sign of v (x2-x1) (VALUE -1,0,1) m = abs(v); // m is the distance between y1 and y2 n = abs(u); // n is the distance between x1 and x2 } s = (int)(m / 2); // s is the m distance (either x or y) divided by 2 for (i=0;i<round(m);i++) { // repeat this loop until it // is = to m (y or x distance) Putpixel(a,b,col); // plot a pixel at the original x1, y1 s += n; // add n (dis of x or y) to s (dis of x of y) if (s >= m) { // if s is >= m (distance between y1 and y2) s -= m; a += d1x; b += d1y; } else { a += d2x; b += d2y; } } } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // Line2() - This function draws a line from x1,y1 to x2,y2 using the // // first method. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Line2(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int col) { int x, y, xlength, ylength, dx, dy; float xslope, yslope; xlength = abs(x1-x2); if ((x1-x2) < 0) dx = -1; if ((x1-x2) == 0) dx = 0; if ((x1-x2) > 0) dx = +1; ylength = abs(y1-y2); if ((y1-y2) < 0) dy = -1; if ((y1-y2) == 0) dy = 0; if ((y1-y2) > 0) dy = +1; if (dy == 0) { if (dx < 0) for (x=x1; x<x2+1; x++) Putpixel (x,y1,col); if (dx > 0) for (x=x2; x<x1+1; x++) Putpixel (x,y1,col); } if (dx == 0) { if (dy < 0) for (y=y1; y<y2+1; y++) Putpixel (x1,y,col); if (dy > 0) for (y=y2; y<y1+1; y++) Putpixel (x1,y,col); } if ((xlength != 0) && (ylength != 0)) { xslope = (float)xlength/(float)ylength; yslope = (float)ylength/(float)xlength; } else { xslope = 0.0; yslope = 0.0; } if ((xslope != 0) && (yslope != 0) && (yslope/xslope < 1) && (yslope/xslope > -1)) { if (dx < 0) for (x=x1; x<x2+1; x++) { y = round (yslope*x); Putpixel (x,y,col); } if (dx > 0) for (x=x2; x<x1+1; x++) { y = round (yslope*x); Putpixel (x,y,col); } } else { if (dy < 0) for (y=x1; y<x2+1; y++) { x = round (xslope*y); Putpixel (x,y,col); } if (dy > 0) for (y=x2; y<x1+1; y++) { x = round (xslope*y); Putpixel (x,y,col); } } } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // Circle() - This draws a circle with center X,Y, with Rad as its radius. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Circle(int X, int Y, int rad, int col) { float deg = 0; do { X = round(rad * cos(deg)); Y = round(rad * sin(deg)); Putpixel (X+160, Y+100, col); deg += 0.005; } while (deg <= 6.4); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // // WaitRetrace() - This waits until you are in a Verticle Retrace. // // // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void WaitRetrace() { _DX = 0x03DA; l1: asm { in al,dx; and al,0x08; jnz l1; } l2: asm { in al,dx; and al,0x08; jz l2; } }